7 Business Intelligence and Analytics
Learning Objectives
- Define big data and its impact on business.
- Explain business intelligence and analytics.
- Understand data warehouses and data mining.
- Describe dashboards and scorecards.
- Demonstrate knowledge of predictive analytics.
Introduction
Business intelligence is important for organizations as it provides critical insights into the performance of their business, customers, competitors, and industry. It helps businesses to make data-driven decisions, mitigate risks, and identify new opportunities for growth – ultimately leading to a competitive advantage.
Here are some ways businesses utilize business intelligence to gain a competitive advantage:
Improved Decision Making: By analyzing data from different sources, businesses can make informed decisions on issues like pricing strategy, inventory management, and marketing campaigns. This leads to better allocation of resources, reduced costs, and increased profits.
Better Customer Insights: Business intelligence enables organizations to understand their customers better by analyzing their behavior, needs, demographics, and preferences. This information helps businesses tailor their products and services to meet customer needs, driving customer loyalty and repeat business. 
Competitive Analysis: Business intelligence tools allow businesses to monitor their competitors’ performance, pricing strategies, and market trends. By keeping tabs on competitors, businesses can adapt their strategies to stay ahead in the market.
Improved Operational Efficiency: Business intelligence helps businesses identify inefficiencies in their operations and supply chain. By optimizing these processes, businesses can save costs, improve productivity, and produce higher quality products and services.
Predictive Analytics: Through predictive analysis, businesses can anticipate future trends and opportunities. This helps them stay ahead of the curve and take strategic decisions to capitalize on new areas of growth.
In conclusion, Business intelligence provides companies with a significant competitive advantage by providing access to accurate and timely information enabling better decision-making, enhancing customer insights, analysis of competitors and industry trends, improving operations, and predictive analytics, which are essential in business growth and success.
How Do Companies Collect Customer Data?
Companies collect customer information through a variety of methods to support their business intelligence (BI) initiatives. Some common methods include:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems: Companies use CRM systems to collect and manage customer information such as their contact information, demographics, purchase history, preferences, and interactions with the company. 
Sales data: Companies collect sales data through point-of-sale systems, online sales channels, and other transactional systems. This data can provide insights into customer behavior and preferences, sales patterns, and other metrics that can inform BI initiatives.
Web analytics: Companies collect data from website analytics tools such as Google Analytics to track website traffic, user behavior, and other metrics that can provide insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Social media monitoring: Companies monitor social media platforms to gather customer feedback, sentiments, and other information that can help them understand customer needs and preferences.
Customer surveys: Companies conduct surveys to gather customer feedback, opinions, and preferences. This data can be used to support BI initiatives and inform business decisions.
Loyalty programs: Companies use loyalty programs to collect various types of customer data such as demographics, interests, purchase behavior, and transaction history.
Example: Sephora’s “Customer Loyalty” Program
One successful retail company that has effectively used loyalty cards to gather customer data and improve business is Sephora. Sephora is a well-known beauty brand that sells a variety of products, including makeup, skincare, and hair care products.
Sephora’s loyalty program is called Beauty Insider, and it is free for customers to join. By signing up for Beauty Insider, customers receive a loyalty card that they can use to earn points for every dollar they spend at Sephora. Additionally, they receive personalized recommendations, exclusive access to sales and events, and free birthday gifts.
One of the ways Sephora uses customer data gathered through their loyalty program is by providing personalized recommendations. Sephora collects data on each customer’s purchase history and preferences, which are then used to create personalized recommendations for makeup and skincare products that the customer may be interested in buying. This helps customers find products that are tailored to their needs, which improves their overall shopping experience at Sephora.
Another way Sephora uses customer data is by analyzing buying trends to identify popular products and brands. By understanding which products and brands are most popular among their customer base, Sephora can make informed decisions about which products to stock in their stores and online. This ensures that Sephora is always meeting the demands of their customers and staying ahead of emerging trends in the beauty industry.
As we can see, Sephora’s successful use of their Beauty Insider loyalty program showcases the power of customer data in improving business. By providing personalized recommendations and understanding customer buying trends, Sephora has been able to create a loyal customer base that keeps coming back for more.
Big Data and Its Impact on Business
Big data refers to the large and complex datasets that are generated from various sources, such as social media platforms, customer transactions, internet of things (IoT) devices, and machine-generated data. These datasets are characterized by their size, complexity, and speed, which make them difficult to manage and analyze using traditional data processing tools.
 The impact of big data on businesses has been transformative. Today, businesses of all sizes and industries are using big data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational performance. With the help of big data analytics, businesses can make data-driven decisions that lead to better customer experiences, increased efficiency, and improved business outcomes.
The impact of big data on businesses has been transformative. Today, businesses of all sizes and industries are using big data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational performance. With the help of big data analytics, businesses can make data-driven decisions that lead to better customer experiences, increased efficiency, and improved business outcomes.
One of the primary ways big data is impacting business is through enhanced customer experiences. By analyzing customer behavior, businesses can gain insights into what their customers want and need. These insights can be used to create personalized experiences that meet customer expectations. For example, retailers can use big data analytics to understand shoppers’ purchase histories, preferences, and behaviors, and then use this information to recommend products, create targeted marketing campaigns, and even design personalized shopping experiences.
In addition to improving customer experiences, big data analytics is also helping businesses to optimize their operational performance. By tracking and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can gain insights into how they can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. For example, manufacturers can use big data analytics to optimize their supply chain, reduce waste, and improve production efficiency. Banks and financial institutions can use big data to detect fraudulent activities, assess credit risk, and improve customer service.
Another major impact of big data on businesses is the ability to gain real-time insights. With the help of big data analytics platforms, businesses can collect and analyze data in real-time, enabling them to make faster, more informed decisions. For example, a retailer can use real-time data to track inventory levels, optimize pricing, and adjust advertising campaigns based on real-time market trends.
The rise of big data has also led to new business models and revenue streams. For example, companies like Amazon and Google have built their businesses around the analysis of vast amounts of data. They use this data to create personalized experiences for their users, improve their algorithms, and generate new revenue streams through data-driven advertising.
Despite the many benefits of big data analytics, there are also a number of challenges that businesses must overcome. One of the biggest challenges is the data itself. Big data is often fragmented, incomplete, and difficult to integrate, which poses a challenge for businesses looking to leverage it for insights and decision-making. In order to effectively harness the power of big data, organizations must invest in the right tools and technologies to manage and integrate the data from various sources. This includes implementing data warehousing solutions, using data integration tools, and utilizing data quality processes to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Furthermore, businesses must also have the expertise and talent to analyze and interpret the vast amounts of data. This requires skilled data scientists, analysts, and engineers who can identify patterns, trends, and insights buried within the data. Without the right people in place, businesses may not be able to fully leverage the potential of big data.
Lastly, it’s important for businesses to have a clear understanding of their goals and objectives when it comes to big data. Simply collecting and storing massive amounts of data isn’t enough – there must be a specific purpose and strategy behind the data collection and analysis. By defining clear goals and objectives, businesses can ensure they are utilizing big data effectively to gain valuable insights and make more informed decisions.
Example: How Tesla Uses Big Data
Tesla is a US-based electric car manufacturer that was founded in 2003. It has been successful in the industry due to its focus on technology, innovation, design, and sustainability.  Tesla is one of the most talked-about companies worldwide, not only because of its eclectic products but also for its strategic use of big data for competitive advantage.
Tesla is one of the most talked-about companies worldwide, not only because of its eclectic products but also for its strategic use of big data for competitive advantage.
Tesla is one of the few companies that have embedded big data analytics into its business processes. The company uses data analytics technologies to improve its processes and products continuously. By collecting, analyzing, and processing large amounts of data from various sources, Tesla can make informed decisions and gain insights into its customers, markets, and trends.
Tesla has designed a data-driven development process that enables it to collect and analyze data from various sensors and sources fitted in their cars. This data, coupled with machine learning algorithms, enables Tesla to improve its products, optimize energy usage, and provide personalized services to customers. Tesla’s data-driven approach to product development has helped it to create cars with longer driving ranges, enhance safety, improve performance, and minimize maintenance costs.
Tesla uses customer data to offer personalized services and experiences to its users. Tesla cars are integrated with sensors and Wi-Fi connectivity, which collects and transmits data to Tesla’s servers. This data is then analyzed to provide recommendations on route planning, charging stations, maintenance needs, and even providing software updates remotely. The feedback collected from customers further helps Tesla to improve its products and services to meet their changing needs.
Tesla uses big data analytics to optimize its supply chain management, production, and logistics. The company uses predictive analytics to forecast demand, production requirements, and to enhance its inventory management. Tesla also uses data analytics and automation to improve the production process, which has streamlined its operations and increased its efficiency.
Tesla’s use of big data analytics has given it a competitive edge in the electric vehicle market. The insights derived from data analytics give the company a clear understanding of the market trends, customer demands, and preferences, which helps it to remain ahead of the curve.
Tesla’s innovative use of big data analytics has transformed the automotive industry. The company’s ability to collect, analyze, and derive insights from data has enabled it to make data-driven decisions that have increased operational efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer experience. Additionally, the company has been able to identify new business opportunities and tailor its products and services to meet customers’ needs better.
Data Warehouses and Data Mining
Data mining is the process of discovering patterns and associations in large sets of data, using techniques from statistics and machine learning. It involves the extraction of meaningful insights and actionable information from data that may otherwise be too complex to be interpreted by humans.
 Data mining has become a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes and across a range of industries, as it can provide insights into customer behavior, market trends, and business operations that can be used to guide decision-making and improve performance.
Data mining has become a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes and across a range of industries, as it can provide insights into customer behavior, market trends, and business operations that can be used to guide decision-making and improve performance.
One of the key benefits of data mining is that it allows businesses to identify patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent. For example, a company may be able to identify which products or services are most popular among different customer segments, which sales channels are most effective, and which marketing campaigns are yielding the highest returns on investment.
Data mining also enables businesses to identify potential problems or issues at an early stage, allowing them to take corrective action before they impact the bottom line. For instance, data mining can be used to detect anomalies in customer behavior or sales trends that may indicate fraudulent activity or other issues that need to be addressed.
Another advantage of data mining is that it can help businesses to predict future outcomes with greater accuracy. By analyzing past data and identifying patterns that are likely to repeat themselves, businesses can make more informed decisions about future investments and strategies.
There are a range of techniques and algorithms that can be used for data mining, depending on the specific goals and objectives of the analysis. Some of the most common techniques include association rule mining, cluster analysis, classification, regression, and neural networks.
Association rule mining involves identifying relationships between different variables in a dataset, such as items that are frequently purchased together or words that tend to appear together in text documents.
Cluster analysis involves grouping data points into clusters based on similarities or differences among them. This can be useful for identifying customer segments or market niches that have distinct needs or preferences.
Classification involves assigning data points to predefined categories based on certain characteristics or attributes. This can be used to predict which customers are most likely to buy a product or to identify fraudulent activity in financial transactions.
Regression is a statistical technique that involves modeling the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. This can be used to predict future outcomes based on past data.
Neural networks are a type of machine learning algorithm that are loosely modeled on the structure and function of the human brain. They can be used for a range of applications, including image and speech recognition and natural language processing.
Data mining is an essential tool for businesses to gain insights into their operations and make informed decisions based on reliable information.
Example: Data Mining at Netflix
 Netflix is a streaming service that offers millions of TV shows and movies to its subscribers. One of the biggest challenges for Netflix was to retain its existing subscribers and expand its customer base. In order to achieve this goal, the company needed to offer personalized recommendations to its users.
Netflix is a streaming service that offers millions of TV shows and movies to its subscribers. One of the biggest challenges for Netflix was to retain its existing subscribers and expand its customer base. In order to achieve this goal, the company needed to offer personalized recommendations to its users.
Netflix understood that every user has unique interests and preferences, and the company needed a way to analyze every user’s viewing habits, in order to tailor its recommendations to each individual user. To achieve this goal, Netflix employed data mining techniques. The company used machine learning algorithms to analyze the viewing habits of millions of users. The algorithms analyzed data such as what users watched, when they watched, and how long they watched.
Netflix used this data to create a sophisticated recommendation engine that served up personalized recommendations to each user. Netflix’s recommendation engine was so effective that the company claims that 80% of the content watched on its platform is a result of recommendation algorithms.
Netflix’s data mining efforts have also helped the company to optimize its content creation strategy. The company analyzed data on user viewing habits to identify the types of content that were most popular with its users.
Based on this analysis, Netflix started to create more original content and licensed more content in genres that were popular with its users. This strategy has paid off for the company, as its original content has won multiple awards and helped to cement its position as a leading streaming service.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is the process of presenting data in a visual format, such as charts, graphs, and maps, to help businesses understand patterns and trends in their operations. Data visualization is important to business decision-making for several reasons: 
Clarity: Data visualization can provide businesses with a clear, concise, and intuitive way to understand complex data, making it easier to identify patterns and trends.
Insight: Data visualization can help businesses gain insights into different aspects of their operations, such as sales performance, customer behavior, and market trends.
Communication: Data visualization can help businesses communicate their findings and insights to stakeholders, such as employees, investors, and customers, in a clear and effective way.
Speed: Data visualization can help businesses quickly identify trends and patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions faster.
Data visualization tools include:
Charts and graphs: Charts and graphs can be used to represent data in a visual format, such as bar charts, line charts, and pie charts.
Dashboards: Dashboards can provide a visual summary of different aspects of business operations, such as sales performance and customer behavior.
Maps: Maps can be used to visualize geographic data, such as customer locations and sales territories.
Dashboards and Scorecards
Dashboards can display a wide range of information, depending on the business needs and objectives. Some common types of information displayed on a dashboard include:
Sales performance: This includes metrics such as revenue, sales growth, conversion rates, and average order value. These metrics can help businesses track their sales performance over time, identify opportunities for growth, and optimize their sales strategies.
Financial health: This includes metrics such as cash flow, profit margins, and expenses. These metrics can help businesses monitor their financial health, identify areas where they can reduce costs, and make informed decisions about investments and resources.
Customer behavior: This includes metrics such as customer satisfaction, retention rates, and purchase history. These metrics can help businesses understand their customers’ needs and preferences, personalize their interactions, and improve customer loyalty.
Marketing performance: This includes metrics such as website traffic, social media engagement, and email open rates. These metrics can help businesses measure the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns, identify opportunities for improvement, and optimize their marketing strategies.
Operations performance: This includes metrics such as production efficiency, inventory levels, and supply chain performance. These metrics can help businesses optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Dashboards are used in business to provide real-time insights into their operations, enabling business users to monitor and analyze their performance, identify opportunities for improvement, and make informed decisions.  
Dashboards are used by various business functions, such as marketing, sales, finance, and operations, to analyze their data and gain insights that can drive business growth and performance.
Dashboards are also used for strategic planning, goal setting, and performance management. By tracking KPIs and metrics on a dashboard, businesses can set targets, monitor progress, and adjust their strategies as needed to achieve their goals.
In conclusion, a business dashboard is an important tool for businesses to monitor and analyze their performance, gain insights into their operations, and make informed decisions. Dashboards display a wide range of information, including sales performance, financial health, customer behavior, marketing performance, and operations performance, allowing business users to track their KPIs and metrics in real-time.
Scorecards
Data scorecards are a tool used in business to track and measure performance against specific goals or targets. They are essentially a visual representation of key performance indicators (KPIs) used to measure success or progress.
Data scorecards typically consist of a series of metrics or KPIs, often represented as graphs or charts, that are regularly updated and reviewed to assess performance in different areas of the business. Examples of metrics that might be included in a data scorecard include sales figures, customer satisfaction ratings, employee turnover rates, and profit margins.
By tracking and analyzing these metrics over time, business owners and managers can quickly identify areas where performance is falling short of expectations and make informed decisions about how to improve. Data scorecards are typically used in conjunction with other business intelligence tools, such as dashboards and reports, to provide a complete picture of performance across an organization.
Example: The “Balanced Scorecard”
Example: The “Balanced Scorecard”
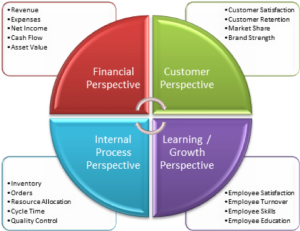
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management tool that helps organizations achieve their objectives and track progress using a set of key performance indicators (KPIs). The Balanced Scorecard framework was first introduced by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton in 1992 in a Harvard Business Review article.
The framework includes four key areas that should be balanced to achieve success: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. The Financial perspective measures the financial performance of the organization through metrics such as revenue, profit, and return on investment. The Customer perspective measures the organization’s ability to meet customer expectations, using metrics such as customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. Internal processes involve identifying and measuring key processes that contribute to delivering value to customers, such as quality, efficiency, and innovation. Finally, Learning and Growth perspective measures the organization’s ability to learn, grow and innovate, using metrics such as employee training and development, leadership, and culture.
The Balanced Scorecard can be used by businesses to develop and track their strategies, communicate objectives to stakeholders, and align employee behaviors with the company’s goals. By measuring KPIs across all areas, organizations can identify areas of improvement, make informed decisions, and track their progress towards achieving their goals. The Balanced Scorecard can also be used to motivate employees, increase accountability, and enhance communication and collaboration within the organization.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is a statistical and analytical approach used to analyze current and historical data to generate insights and predictions about future events or business outcomes. It uses various techniques such as data mining, machine learning, and statistical modeling to understand trends and patterns in data and predict the likelihood of future events.
Predictive analytics works by analyzing a large amount of data to identify patterns and relationships, which are then used to create models that can predict future behavior. These models are then tested against the relevant data to determine their accuracy and refine the algorithms.
In business, predictive analytics is used to optimize decision-making, identify trends, minimize risks, and improve performance by predicting future outcomes. This can be applied to various business areas such as sales and marketing, supply chain management, fraud detection, customer retention, and staffing optimization. For example, companies can use predictive analytics to forecast sales and demand, identify churn risks among customers or improve the accuracy of inventory management.
Example: Predictive Analytics at UPS
 One notable example of a company using predictive analytics for success is UPS. UPS has been using predictive analytics technology for years to optimize its delivery routes, reduce fuel consumption, and better manage its fleet of vehicles.
One notable example of a company using predictive analytics for success is UPS. UPS has been using predictive analytics technology for years to optimize its delivery routes, reduce fuel consumption, and better manage its fleet of vehicles.
UPS uses a custom-built advanced analytics platform called ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation). ORION utilizes historical data on millions of packages, delivery routes, and other key factors to help UPS drivers plan their delivery routes for maximum efficiency.
The platform leverages machine learning algorithms to constantly improve its accuracy and can take into account real-time factors like traffic, weather, and road closures to make adjustments on the fly.
By using ORION, UPS has been able to reduce its total miles driven by over 100 million each year, resulting in a reduction of 10 million gallons of fuel usage per year, and cutting carbon emissions by 100,000 metric tons annually.
Predictive analytics has also helped UPS streamline its supply chain operations by allowing the company to forecast demand, anticipate supply chain disruptions, and optimize inventory levels. These improvements have saved the company billions of dollars over the years and continue to drive its success.
Summary
Business intelligence and analytics are two critical concepts that together assist enterprises in making data-driven decisions, improving business performance, customer satisfaction, and building competitive advantage. Business intelligence refers to the process of warehousing, integrating, and analyzing data from internal and external sources to gain insights into business operations. It enables organizations to optimize their resources by providing a comprehensive view of their business processes, customers, and market trends.
Analytics, on the other hand, is a subset of business intelligence that involves the use of quantitative and qualitative methods to extract insights from data. Analytics is the process of identifying patterns in the data to improve decision-making, forecasting, and strategic planning. It uses different techniques such as descriptive and predictive, analytics to derive insights from data.
Descriptive analytics is used to summarize historical data, identify trends, and provide insights into what happened. It involves the use of techniques such as data visualization, dashboards, and reports. Predictive analytics, on the other hand, predicts future events using historical data and statistical algorithms. It uses techniques such as data mining, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to make predictions.
The business intelligence and analytics market is rapidly growing due to the need for enterprises to gain insights from their data to drive business growth. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global business intelligence market is expected to grow from $23.1 billion in 2020 to $33.3 billion by 2025. The report also suggests that the growth of the market is attributed to the increasing demand for cloud-based business intelligence solutions, advanced analytics techniques, and the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies.
Discussion Questions:
- What is business intelligence and how can it be used to improve organizational performance?
- What is big data and how has it changed the way companies approach decision-making?
- How does data mining differ from traditional statistical analysis?
- How can visualization be used to communicate insights from data?
- What are the ethical considerations of using data analytics in business?
- What is machine learning and how can it be used in business intelligence?
- How can companies maximize the value of their data assets?
- What are some common challenges companies face when implementing business intelligence and analytics solutions?
- How can businesses use predictive analytics to identify patterns and trends?

