1 Introduction to Business Information Systems
Learning Objectives
- Define business information systems.
- Describe the history of information systems and their evolution.
- Identify the basic components of information systems.
- Differentiate between types of information systems.
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital age, information has become the most valuable asset for individuals, organizations, and governments. It is an essential tool for decision-making, communication, and managing business processes. This has led to the development of Information Systems (IS) – a field that combines computer science, business management, and information technology to create systems that support decision-making and business processes.
Information systems have become an essential aspect of modern business operations. They have revolutionized the way that organizations operate, communicate, and store and analyze data. IS provides platforms for gathering, processing, and distributing information and have enabled businesses to operate more efficiently and effectively.
What is an Information System?
An information system is a set of hardware, software, data, procedures, and people that are organized to collect, process, store, and disseminate information to support decision-making, coordination, control, analysis, and visualization in an organization.
Information Systems (IS) are critical to the success of an organization, offering a range of functions that cannot be performed without them. For example, IS can be used to automate administrative tasks, analyze data to improve strategic planning, provide real-time decision support, and facilitate communication and collaboration between employees, customers, and suppliers.
The field of information systems is broad, covering various domains such as healthcare, finance, education, logistics, marketing, supply chain, and others. In each domain, information systems are used to provide unique solutions that help solve specific problems and attain specific goals.
Information Systems in Healthcare
Healthcare relies heavily on IS to manage patient records, billing, insurance claims, and to coordinate healthcare services across multiple providers. Information systems in healthcare are designed to improve patient safety, enhance patient care, increase operational efficiency, and reduce costs. Moreover, IS can support medical research, clinical trials, and public health initiatives by providing access to data and information that can be analyzed to detect trends, identify insights, and facilitate evidence-based decision making.
Information Systems in Finance
In finance, IS are used for a range of functions such as accounting, financial reporting, risk management, and investment analysis. Financial institutions rely on complex and sophisticated IS to manage large volumes of transactions, process loans, and monitor investment portfolios. Information systems in finance are designed to reduce operational risk, increase financial transparency, and drive profitability while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Information Systems in Education
In education, IS are used to support teaching, learning, and research. Educational institutions use IS to manage student records, curriculum development, and student information systems. IS in education are designed to provide access to information, promote collaborative learning, increase student engagement, and improve learning outcomes.
Information Systems in Supply Chain and Logistics
In logistics and supply chain management, IS are used to manage inventory, track shipments, and optimize transportation routes. Information systems in this field are designed to increase supply chain visibility, reduce costs, boost efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Information Systems in Marketing
Marketing, on the other hand, uses information technology to create, distribute and promote products or services to customers. Information technology has allowed marketers to collect and analyze data about consumer behavior, preferences and habits, leading to more targeted and effective marketing campaigns.
Information Systems in the Enterprise
Information technology has also led to the development of various types of information systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and supply chain management (SCM) systems. These systems help organizations to manage their operations efficiently and effectively, improving their performance and competitiveness.
Information systems technology plays a vital role in modern organizations as it enables them to manage their resources, analyze data, and make informed decisions. The successful integration of information systems technology and information systems can lead to improved efficiency, productivity, and profitability for organizations.
Example: Uber
Uber is a ride-hailing company that was founded in San Francisco, California in 2009. The company’s core business model is to connect passengers with drivers through a mobile app, making it easy for people to get around cities quickly and affordably.
Uber’s competitive advantage is built on its ability to harness the power of Information Systems to create a user-friendly platform that connects drivers and passengers in real-time. The company has developed an Information System that integrates multiple technologies such as GPS, mapping, and mobile payments, making it easy for users to order a ride, track their driver’s location, and pay for their trip through the app. Uber has been able to leverage Information Systems in several ways to achieve competitive advantage. These include:
Data Collection and Analysis
Uber collects vast amounts of data from its users, including location data, trip data, and payment data. The company uses this data to optimize its service, improve driver and passenger experiences, and make informed decisions about its business operations.
For example, Uber uses data analytics to track demand patterns and adjust pricing in real-time to ensure that there is always a supply of drivers available when and where they are needed. The company also uses data to improve driver retention by providing them with incentives and optimizing their routes to reduce wait times and increase earnings.
Real-Time Tracking and Communication
One of the unique features of Uber’s Information System is the ability to track drivers and passengers in real-time. This allows customers to know exactly when their ride will arrive and enables drivers to find their passengers easily.
The real-time tracking also allows Uber to monitor drivers’ behavior and ensure that they are following the company’s safety and quality standards. The company can quickly intervene if there are any issues such as accidents or improper behavior, ensuring a high level of safety and security for both drivers and passengers.
Seamless Payment Integration
Uber’s Information System makes it easy for passengers to pay for their rides through the app, without the need for cash or credit cards. The app securely stores payment information and automatically charges the passenger’s account at the end of each trip.
This seamless payment integration not only improves the customer experience but also helps to reduce fraud and improve financial transparency for both Uber and its drivers.
Dynamic Pricing
Uber’s Information System allows the company to implement dynamic pricing, which adjusts fares in real-time based on supply and demand. This means that when there are a lot of people requesting rides at a particular time and in a particular location, the fare will go up to incentivize more drivers to come to that location and meet the demand. Conversely, when there are fewer people requesting rides, the fare will go down to encourage more people to take rides. This system benefits both drivers and riders: drivers earn more money during peak times, and riders have access to more cars when demand is high.
Additionally, Uber’s Information System tracks various data points about rides, such as pickup and drop-off locations, fare amounts, and driver ratings. This data is used to improve the overall experience for both drivers and riders. For example, Uber uses data analysis to identify locations where drivers are most in demand and offers incentives to drivers who are willing to pick up passengers in those locations. The company also uses data to develop new services, such as UberPOOL, which allows riders to share rides with other passengers on the same route.
In conclusion, Uber’s Information System is a critical component of the company’s success. By using data to offer dynamic pricing, improve driver and rider experiences, and develop new services, Uber is able to stay ahead of the competition in the rapidly evolving ridesharing market.
The History and Evolution of Information Systems
Information systems have come a long way since their inception in the 1950s. The evolution of these systems can be traced through various technologies that have been invented, improved, and adapted over time. From punch cards to modern-day big data analytics, the advancements in computing and communication technologies have led to the emergence and continual transformation of information systems.
1950s to 1970s
Information systems first emerged during the 1950s with the introduction of punched cards, which were used for data storage and processing. This evolved into batch processing systems, where data was processed in large batches without any real-time feedback. As computing technologies advanced, interactive systems were introduced where users could interact with the computer in real-time.
During the 1960s, the concept of a database was introduced, where data could be stored in a structured manner and retrieved as and when required. This was a significant development that enabled businesses to store and manage a vast amount of data. The 1970s saw the emergence of online transaction processing (OLTP) systems, which allowed businesses to process transactions online in real-time. This marked the beginning of computerized business processes and revolutionized the way businesses operated.
1980s to early 2000s
The 1980s saw the advent of personal computers (PCs), which made computing much more accessible to individuals and small businesses. This marked the beginning of distributed computing, where multiple computers could share resources and work together. The introduction of Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) enabled users to communicate, access data, and share resources across geographically dispersed locations.
During the 1990s, the introduction of the World Wide Web brought about significant changes in the way people accessed and shared information. This resulted in the development of web-based information systems that allowed businesses to share information and data with internal and external stakeholders. The emergence of electronic commerce (e-commerce) made it possible for businesses to sell products and services online and opened up new markets and revenue streams.
The early 2000s saw the emergence of mobile computing, where users could access information and services through mobile devices. This led to the development of mobile applications and mobile information systems that made it possible for businesses to reach customers on the move.
Late 2000s to Present
The late 2000s saw the rise of social media, which enabled users to create and share content and connect with others. This led to the development of new information systems designed to manage and analyze social media data. Social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram employed advanced algorithms that could track user behavior and target relevant ads based on their interests and preferences.
In addition, cloud computing became more prominent during this era, providing a new way for businesses to store and access data. This opened up new possibilities for collaboration and remote work, allowing teams to access information from anywhere in the world.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning also started to gain widespread use during this period, particularly in industries such as finance, healthcare, and marketing. These tools allowed for the analysis of vast amounts of data, helping businesses make more informed decisions based on insights and patterns.
The present day continues to see advancements in information systems, with the increasing use of IoT devices and the development of blockchain technology. IoT devices, such as smart sensors and wearables, generate a massive amount of data, which can be leveraged to improve efficiency, personalize products and services, and reduce costs.
Blockchain technology, on the other hand, offers a secure and decentralized way to record and store data. It has the potential to transform industries such as banking, supply chain management, and healthcare by providing transparent and immutable records that can reduce fraud, errors, and other security risks.
The evolution of information systems has been transformative, enabling businesses and individuals to access, analyze, and use data in ways that were once unimaginable. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for innovation and growth are endless.
Impact of Information Systems on Business
The impact of technology on business has been far-reaching and widespread. Here are some of the important ways that technology has impacted business since 1980:
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Technology has enabled businesses to automate and streamline many of their processes, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing productivity. For example, accounting software can automate bookkeeping tasks, while customer relationship management (CRM) software can help businesses manage customer interactions more effectively.
Improved Communication and Collaboration: Technology has made it easier for businesses to communicate and collaborate with employees, partners, and customers. Email, instant messaging, and video conferencing technologies have enabled remote communication and collaboration, while collaborative software tools like Google Drive and Microsoft Teams have made it easier for teams to work together on projects in real-time, regardless of their physical location.
Increased Globalization: The internet has enabled businesses to reach a global audience and tap into new markets. E-commerce sites like Amazon and Alibaba have made it easy for businesses to sell products worldwide, while online marketplaces like Upwork and Fiverr have made it possible for businesses to access a global workforce.
Improved Customer Experience: Technology has enabled businesses to provide a more personalized and convenient experience for their customers. For example, businesses can use data analytics and machine learning to offer personalized product recommendations, while chatbots and other AI-based technologies can provide quick and efficient customer support.
Reduced Costs: Technology has enabled businesses to reduce costs in many areas, from supply chain management to marketing and advertising. By leveraging automation, analytics, and cloud computing, businesses can minimize their expenses and improve their bottom line.
In summary, the history of business and technology since 1980 has been characterized by rapid innovation and evolution. As new technologies continue to emerge, businesses must continually adapt to stay competitive and meet the changing needs of their customers.
Example: Rise and Fall and Return of Dell Computer

Dell is a well-known computer company that was founded in 1984 by Michael Dell. It started as a small business in his college dorm room and grew rapidly to become a leading computer manufacturer. Dell’s business model was based on selling directly to consumers and businesses, bypassing traditional retail channels. This allowed the company to offer lower prices and more customization options for its products.
Rise of Dell
Throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, Dell experienced rapid growth and became one of the most successful PC manufacturers in the world. The company’s direct-to-consumer sales model gave it a competitive advantage over competitors like IBM and Compaq, which relied on third-party retailers. Additionally, Dell was able to offer customers more customization options than its competitors, allowing them to choose specific components and configurations for their computers.
One of Dell’s key competitive advantages was its supply chain management system. The company had established relationships with component suppliers and manufacturers, allowing it to quickly assemble and ship custom-configured computers to customers. This helped Dell to reduce costs and improve delivery times, giving it an edge in the market.
By 2001, Dell had become the world’s largest PC manufacturer, with revenues of over $31 billion. The company’s success had made Michael Dell one of the richest people in the world, with a net worth of around $18 billion.
However, Dell’s success would not last forever.
Fall of Dell
In the mid-2000s, Dell began to experience problems with its business model. The company’s focus on cost-cutting and efficiency had led to a lack of innovation, with its products becoming seen as uninspiring and outdated. Additionally, competitors like Apple were gaining market share by offering more innovative and stylish products.Dell’s direct-to-consumer sales model also began to lose its competitive advantage. As more and more retailers began to sell computers online, Dell found itself facing increasing competition from companies like Amazon and Best Buy. Additionally, customers began to demand more personalized support and service, which Dell was unable to provide with its online-only sales model.
Another issue facing Dell was its lack of focus on emerging markets like mobile devices and cloud computing. As these technologies became more important, Dell found itself falling behind competitors like Apple and Google.
Return of Dell
In 2010, Michael Dell returned to the company as CEO, with the goal of turning things around. He began to focus on innovation and design.
He identified that Dell’s competitors were innovating faster than his company, and that Dell’s slow-moving bureaucracy was hindering its ability to keep up with the market. To combat this, Dell began investing heavily in research and development, as well as in design.
Under Dell’s leadership, the company began to introduce new products and redesign existing products to be more visually appealing and user-friendly. The new focus on design was evident in the company’s flagship laptop, the XPS 13, which received praise for its sleek design and premium materials.
In addition to design, Dell also emphasized sustainability as a key part of the company’s strategy. The company worked to reduce its carbon footprint by implementing energy-efficient technologies and reducing waste.
These efforts paid off: Dell’s revenue grew steadily under Michael Dell’s leadership, and the company went private in 2013 in a leveraged buyout. Today, Dell is a leading global technology company, providing everything from personal computers and servers to storage systems and networking products.
Impact of Information Systems on Traditional Business Careers
Modern technology has had a significant impact on various business careers, including finance, accounting, marketing, operations, and human resources. Here are some examples of how technology has affected these careers:
Finance: Technology has revolutionized the finance industry by enabling businesses to automate and streamline financial processes, reduce costs, and improve decision-making. For example, financial software can automate tasks such as bookkeeping, tax preparation, and financial analysis. Data analytics tools can help businesses analyze financial data to identify trends and make informed decisions.
Accounting: Like finance, accounting has seen significant changes due to technology. Accounting software can automate repetitive tasks such as data entry and reconciliation, improving accuracy and efficiency. Cloud-based accounting systems allow businesses to access their data from anywhere and collaborate with their accountants or bookkeepers in real-time.
Marketing: Technology has had a profound impact on marketing, opening up new channels of communication and enabling businesses to reach wider audiences. Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have provided businesses with new ways to connect with customers and build brand awareness. Data analytics tools allow businesses to analyze customer behavior and preferences, creating opportunities for personalized marketing campaigns.
Operations: Technology has played a crucial role in improving operational efficiency and reducing costs. Automation technologies, such as robotics and artificial intelligence (AI), can streamline manufacturing processes, improve product quality, and reduce waste. Advanced analytics tools can help businesses optimize production schedules and supply chain management.
Human Resources: Technology has enabled HR departments to automate many administrative tasks, such as payroll processing and benefits administration. Online recruiting platforms, such as LinkedIn and Glassdoor, have made it easier for companies to find and attract qualified candidates. Data analytics tools can help HR departments identify skill gaps and identify opportunities for employee development.
In conclusion, modern technology has had a significant impact on various business careers, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling businesses to make informed decisions. As technology continues to evolve, businesses must continue to adapt to stay competitive and meet the changing needs of their customers.
Information Systems Careers
Information technology careers encompass a wide range of job opportunities, from software development and programming to cybersecurity and network administration. Here are some examples of modern IT careers:
Software Development: Software developers create and maintain software programs that organizations use to perform various tasks. They work with programming languages such as Java, Python, and C++ to develop applications for desktop and mobile devices.
Cybersecurity: As organizations rely more on technology to store and manage sensitive information, the need for cybersecurity professionals has grown. Cybersecurity experts protect networks, systems, and data from unauthorized access, theft, and damage.
Data Analytics: Data analysts work with large sets of data to identify patterns and trends, which organizations can use to make informed decisions. They use tools such as SQL, Python, and R to extract, transform, and analyze data from various sources.
Network Administration: Network administrators are responsible for maintaining the technology infrastructure of an organization. They manage servers, routers, switches, and other networking components to ensure that systems are running efficiently and securely.
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing professionals manage cloud-based infrastructure and services. They work with technologies such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform to help organizations store data, run applications, and manage their IT resources more efficiently.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of IT careers available in today’s job market. As technology continues to evolve, there will be a growing demand for skilled IT professionals who can adapt to new technologies and help organizations meet their business goals.
Basic Components of Information System
An Information System is a set of interconnected elements and technologies that collect, process, store, and disseminate data and information. It is a combination of hardware, software, data, people, and processes that work together to create a system that supports the goals of an organization. An Information System has several component parts, including: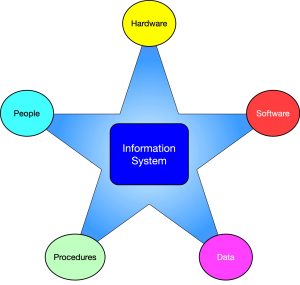
Hardware: This consists of physical components such as computers, servers, routers, switches, printers, scanners, and other peripheral devices that are used to process, store, and output data.
Software: This refers to the programs and applications that are used to manipulate and control data in an information system. Software can be divided into two categories: system software and application software. System software controls the hardware and provides a platform for the application software to run. Application software is used for specific tasks such as word processing, accounting, inventory management, and so on.
Data: These are raw facts or figures that are unorganized and meaningless on their own. Data can come in various forms such as text, numbers, images, audio or video. Data is stored and processed by the Information System. It can be structured or unstructured, and may include customer data, financial records, inventory, and other critical information.
People: This includes all the individuals who interact with the Information System, from users who input data to IT professionals who maintain and manage the system.
Processes: This refers to the procedures and protocols that guide the use of the system, including security measures, backup procedures, and data management policies.
Together, these components work together to collect, process, store and disseminate information to the end user. This information can then be used for decision making, analysis, reporting or other business functions.
Types of Information Systems
Information Systems can be found in almost every aspect of modern life. Some examples of Information Systems include:
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS): These are systems that are used to process day-to-day transactions, such as sales, payments, and inventory management. These systems are typically used by retailers, banks, and other organizations that deal with high volumes of transactions. The primary purpose of a TPS is to ensure that all transactions are accurately recorded, processed, and stored for future reference.
Management Information Systems (MIS): This system is used to collect data from different sources, process the information, and present it to the management team for decision making. Businesses use MIS to obtain operational data, financial data, and demographic data that help them to recognize patterns and trends, make informed decisions and answer questions regarding the organization’s operations, customers, markets and financial health. They may include reports, dashboards, and other tools that aggregate data from multiple sources and present it in a format that is easily understandable.
Decision Support Systems (DSS): These are systems that are used to support decision-making. A DSS helps to solve a complex business problem by providing relevant data and analysis tools. It is used in situations where there is no clear answer, and the decision requires extra knowledge and analysis. DSS may include forecasting tools, data analysis tools, and other applications that help users make informed decisions based on data. DSS is often utilized in areas like marketing, finance, and logistics to support complex decision-making, optimization and simulations.
Expert Systems – An expert system deals with knowledge and provides expert advice to non-experts. This system is created to imitate the decision-making process of human experts. These systems are used in specialized areas such as medicine, law or engineering, where the knowledge is too complex for an average individual to understand.
Supply Chain Management Systems: These are systems that are used to manage the flow of goods and services from the point of origin to the point of consumption. They may include tools for tracking inventory levels, coordinating transportation, managing supplier relationships, and optimizing distribution channels.
Office Automation System (OAS) – An OAS helps to automate office operations, such as document preparation, scheduling, messaging, and file maintenance. An OAS allows employees to perform multiple tasks efficiently and effectively, thereby making the office workflow process more efficient. Common examples include word processors, email, and scheduling software.
Summary
This chapter discusses the importance of information systems (IS) in modern society. An IS is defined as a combination of hardware, software, data, procedures, and people used to collect, process, store, and disseminate information to support decision-making, coordination, control, analysis, and visualization in an organization. In today’s society, information is considered the most valuable asset for individuals, organizations, and governments, and IS has emerged and developed to facilitate decision-making, communication, and business processes.
The chapter highlights the importance of IS in various fields, including finance, logistics, and supply chain management. Financial institutions rely on complex and sophisticated IS to manage large volumes of transactions, process loans, and monitor investment portfolios. Similarly, IS in logistics and supply chain management is used to manage inventory, track shipments, and optimize transportation routes, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
The chapter also discusses the various types of IS used in organizations, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and supply chain management (SCM) systems. These systems help organizations manage their operations efficiently and effectively, improving their performance and competitiveness.
Lastly, the chapter traces the evolution of IS through various technologies that have been invented, improved, and adapted over time. From punch cards to modern-day big data analytics, the advancements in computing and communication technologies have led to the emergence and expansion of various types of information systems.
This chapter stresses the pivotal role of IS in facilitating organizational efficiency and effectiveness. As technology continues to advance, organizations will likely continue to adopt and adapt new information systems to meet their evolving needs.
Discussion Questions:
- What are the key advantages of implementing DSS for decision-making in a business?
- How have ERP systems impacted the way businesses manage their resources?
- What are the benefits of using CRM systems to improve customer service?
- How can SCM systems improve supply chain efficiency and effectiveness?
- What role do KMS play in enhancing employee performance and problem-solving within an organization?
- How have information systems impacted organizational efficiency and effectiveness?
- What are the potential risks and challenges associated with implementing new information systems?
- What factors should businesses consider when selecting and adopting new information systems?
- What impact does the evolution of technology have on the adoption and adaption of new information systems in organizations?

