10 Information Systems for Competitive Advantage
Learning Objectives
- Explain how information systems can achieve competitive advantage.
- Describe case studies of organizations using information systems for competitive advantage.
- Understand how to implement information systems for competitive advantage.
- Recognize emerging trends in information systems.
Introduction
Competitive advantage is the ability of a company to outperform its competitors in a given market, by producing goods or services that are of superior quality, at a lower cost, or that provide unique benefits to customers. A company’s competitive advantage can be achieved through various strategies, including differentiation, cost leadership, or focus.
 An example of a company that achieved competitive advantage through differentiation is Apple. Apple differentiates itself from its competitors by developing innovative and high-quality products that offer a unique user experience. Apple’s design and user interface are distinct and recognizable, which helps the company build strong brand recognition and customer loyalty. In addition, Apple’s focus on providing excellent customer service and support further differentiates it from its competitors. These factors have helped Apple maintain its position as a leader in the technology industry and continue to attract a loyal customer base.
An example of a company that achieved competitive advantage through differentiation is Apple. Apple differentiates itself from its competitors by developing innovative and high-quality products that offer a unique user experience. Apple’s design and user interface are distinct and recognizable, which helps the company build strong brand recognition and customer loyalty. In addition, Apple’s focus on providing excellent customer service and support further differentiates it from its competitors. These factors have helped Apple maintain its position as a leader in the technology industry and continue to attract a loyal customer base.
An example of a company that achieved competitive advantage through cost leadership is Walmart. Walmart is known for its low prices and ability to provide goods at a lower cost than its competitors. The company achieves this through various strategies, including effective supply chain management, bulk purchasing, and efficient operations. Walmart’s supply chain is highly optimized to reduce costs, with the company using data and analytics to predict demand and manage inventory effectively. In addition, Walmart purchases goods in bulk, allowing it to negotiate lower prices with suppliers. These strategies have enabled Walmart to offer low prices to its customers, attracting a large customer base and maintaining a competitive edge in the retail industry.
An example of a company that achieved competitive advantage through focus is Southwest Airlines. Southwest Airlines differentiates itself from its competitors by focusing on a specific market segment – short-haul flights within the United States. By focusing on this niche, the company has been able to optimize its operations, making it more efficient and cost-effective than its competitors. This has allowed Southwest Airlines to offer lower fares, which has helped it attract price-sensitive customers. In addition, Southwest Airlines has built a strong brand reputation for its customer service and employee satisfaction, which further strengthens its competitive advantage. By staying focused on its niche market and continuously improving its operations, Southwest Airlines has been able to maintain its position as a leading low-cost carrier in the aviation industry.
Achieving competitive advantage with information systems
Information systems can be used by organizations to gain a competitive advantage in various ways:
Improved Efficiency: Information systems can automate and streamline many business processes, improving efficiency and reducing costs. This means that organizations can produce goods and services at a lower cost than their competitors, which can be a significant competitive advantage.
Enhanced Customer Service: Information systems enable organizations to collect and analyze data about their customers, allowing them to provide more personalized and responsive customer service. This can lead to increased customer loyalty and retention, which can be a key competitive advantage in many industries.
Product Innovation: Information systems can help organizations to innovate by providing insights into customer preferences, market trends, and emerging technologies. This can help organizations to develop new products and services that meet the changing needs of their customers, giving them a competitive advantage.
Faster Decision-Making: Information systems provide real-time data, analytics, and reporting, enabling organizations to make faster and more informed decisions. This can help organizations to respond quickly to market changes and stay ahead of their competitors.
Supply Chain Optimization: Information systems can optimize the supply chain by improving inventory management, reducing lead times, and minimizing waste. This can help organizations to reduce costs, increase productivity, and improve customer satisfaction, all of which can provide a competitive advantage.
In conclusion, information systems can be a powerful tool for organizations to gain a competitive advantage in their industries by improving efficiency, enhancing customer service, fostering innovation, enabling faster decision-making, and optimizing the supply chain.
Michael Porter’s Competitive Advantage Models
Value Chain Model
Michael Porter’s value chain model is a framework that identifies the primary activities and support activities that are required to create value for customers. The primary activities include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, while the support activities include procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure. By analyzing each of these activities and identifying how they can be streamlined or enhanced, a company can create a competitive advantage.
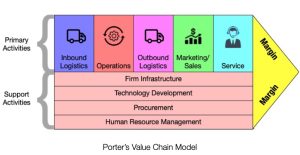
Examples of How Companies Might Use Information Systems in Each Segment of Porter’s Value Chain:
Inbound Logistics: A company might use information systems to track and manage the delivery of raw materials and supplies from suppliers. This can include using barcode scanning technology to track inventory levels, using automated replenishment systems to ensure that supplies are ordered and delivered on time, and using data analytics to forecast demand and optimize inventory levels.
Operations: A company might use information systems to automate and streamline manufacturing processes. This can include using robotics and automation technologies to increase efficiency and reduce waste, using advanced analytics to optimize production schedules, and using quality control systems to monitor and improve product quality.
Outbound Logistics: A company might use information systems to manage the distribution of products to customers. This can include using logistics software to optimize shipping routes and reduce delivery times, using real-time tracking systems to monitor shipments, and using customer relationship management (CRM) tools to manage customer accounts and preferences.
Marketing and Sales: A company might use information systems to target and engage customers. This can include using digital marketing platforms to reach customers through social media, email, and other channels, using data analytics to personalize marketing messages and offers, and using customer feedback systems to collect and respond to customer reviews and complaints.
Service: A company might use information systems to provide customer service and support. This can include using chatbots and other AI-based technologies to provide quick and efficient support, using customer satisfaction surveys to measure and improve service quality, and using customer relationship management (CRM) tools to manage customer accounts and preferences.
Procurement: A company might use information systems to manage the procurement of goods and services from suppliers. This can include using online procurement systems to manage the bidding and purchasing process, using data analytics to forecast demand and optimize inventory levels, and using supplier relationship management (SRM) tools to monitor and manage supplier performance.
Technology Development: A company might use information systems to support research and development (R&D) efforts. This can include using data analytics and machine learning to identify new product opportunities, using simulation and modeling tools to test and optimize product designs, and using collaborative platforms to facilitate cross-functional teamwork and innovation.
Human Resource Management: A company might use information systems to manage its workforce. This can include using HR management software to track employee performance, manage compensation and benefits, and support employee development and training programs.
Five Forces Model
Porter’s five forces model is another framework that helps companies analyze the competitive forces in their industry. The five forces include the bargaining power of suppliers, the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of competitive rivalry. By understanding the dynamics of these forces, a company can make strategic decisions about how to position itself within the market.
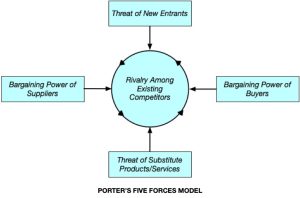
Example of How Companies Might Use Information Systems in Each Segment of Porter’s Five Forces Model:
Bargaining Power of Suppliers: A company might use information systems to manage supplier relationships and negotiate better terms. This can include using supplier relationship management (SRM) tools to monitor and manage supplier performance, using e-procurement systems to streamline the purchasing process, and using data analytics to identify areas for cost savings and optimization.
Bargaining Power of Buyers: A company might use information systems to better understand customer behavior and preferences, and to tailor its offerings accordingly. This can include using customer relationship management (CRM) tools to manage customer accounts and preferences, using data analytics to identify customer trends and patterns, and using digital marketing platforms to reach and engage customers more effectively.
Threat of New Entrants: A company might use information systems to create barriers to entry and establish a strong competitive position. This can include using data analytics to identify gaps in the market and develop new products or services that are difficult to replicate, using patent and trademark systems to protect intellectual property, and using pricing strategies to make it difficult for new entrants to gain market share.
Threat of Substitute Products or Services: A company might use information systems to develop and promote unique features and benefits that differentiate its products or services from those of competitors. This can include using market research to identify opportunities for innovation and differentiation, using design and branding to develop a strong brand identity and customer loyalty, and using digital marketing platforms to communicate the unique value proposition of its products or services.
Intensity of Competitive Rivalry: A company might use information systems to monitor and analyze the competitive landscape, and to make strategic decisions about its pricing, product offerings, and marketing strategies. This can include using data analytics to track the performance of competitors and identify areas for improvement, using automated pricing algorithms to respond to changes in market conditions, and using social media and other digital marketing channels to stay top of mind with customers.
Who is Michael Porter?
Michael Porter is an American academic and management theorist best known for his work on competitive strategy and the five forces model. He earned a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering from Princeton University in 1969, an MBA from Harvard Business School in 1971, and a Ph.D. in business economics from Harvard in 1973.
Porter’s work on competitive strategy has had a profound impact on the business world. His framework helps companies analyze the competitive forces in their industry and make strategic decisions about how to position themselves within the market.
Porter is currently the Bishop William Lawrence University Professor at Harvard Business School, where he teaches courses on competitive strategy and international competitiveness. He has written numerous books and articles on these topics, and his work has been widely cited and influential in the field of management.
Organizations Using IS for Competitive Advantage
Amazon.com
 Amazon is another example of how information systems can be used for competitive advantage. The company has become one of the largest retailers in the world by using information systems to optimize their supply chain, reduce lead times, and provide efficient and personalized customer service.
Amazon is another example of how information systems can be used for competitive advantage. The company has become one of the largest retailers in the world by using information systems to optimize their supply chain, reduce lead times, and provide efficient and personalized customer service.
One of the key ways that Amazon has used information systems for competitive advantage is through the use of data analytics. The company has access to a vast amount of data on customer behavior, order history, and market trends, which they use to continuously improve their services. For example, they use data analytics to track customer preferences and purchase history, allowing them to recommend products that are likely to be of interest to their customers. This has increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, providing a competitive advantage in the market.
Another way that Amazon has used information systems for competitive advantage is through the use of supply chain optimization. By using real-time data analytics, Amazon is able to track inventory levels, optimize distribution, and reduce lead times. This has allowed them to serve customers more quickly and efficiently than their competitors, providing a unique value proposition in the market.
Finally, Amazon has used information systems to provide efficient and personalized customer service. By using data analytics to track customer behavior, Amazon is able to anticipate customer needs and provide recommendations that are tailored to their interests. They also use technology such as chatbots and voice assistants to provide quick and efficient customer support, improving the customer experience and increasing loyalty.
As we can see, Amazon’s use of information systems has enabled them to create a platform that is fast, efficient, and personalized, providing a competitive advantage that has made them one of the largest retailers in the world. By using data analytics and supply chain optimization, they have been able to optimize their operations and improve the customer experience, providing a value proposition that is difficult for their competitors to match.
Uber Ride Sharing
 Uber is a prime example of how information systems can be used for competitive advantage. The company has revolutionized the transportation industry by using a mobile application to match riders with drivers and provide real-time tracking and payment options. Their use of advanced algorithms and data analytics has enabled them to optimize their pricing and supply chain, providing a fast and affordable transportation option that has disrupted the traditional taxi industry.
Uber is a prime example of how information systems can be used for competitive advantage. The company has revolutionized the transportation industry by using a mobile application to match riders with drivers and provide real-time tracking and payment options. Their use of advanced algorithms and data analytics has enabled them to optimize their pricing and supply chain, providing a fast and affordable transportation option that has disrupted the traditional taxi industry.
One of the key ways that Uber has used information systems for competitive advantage is through the use of data analytics. The company has access to a wealth of data on rider behavior, driver performance, and market trends, which they use to continuously refine and improve their services. For example, they use data analytics to monitor demand patterns and adjust pricing, ensuring that they have enough drivers on the road to meet rider demand while also maximizing revenue. They also use data analytics to track driver performance and feedback, ensuring that their drivers are providing a high level of service that meets their customer’s needs.
Another way that Uber has used information systems for competitive advantage is through the use of mobile technology. By providing riders with access to real-time tracking and payment options, Uber has created a user-friendly and convenient platform that has made it easier for riders to book rides and pay for them. This has improved the customer experience and led to increased loyalty and retention.
Finally, Uber has used information systems to optimize their supply chain, reducing costs and providing a competitive advantage in the market. By using real-time data analytics, Uber is able to identify demand patterns and optimize their driver deployment, reducing wait times for riders and increasing driver earnings. They also use data analytics to optimize their pricing, ensuring that they are able to compete effectively with traditional taxi services while also maintaining profitability.
Uber’s experience shows that the use of information systems has enabled them to create a platform that is fast, convenient, and affordable, providing a unique value proposition in the transportation industry. By using data analytics and mobile technology, they have been able to optimize their supply chain and improve the customer experience, providing a competitive advantage that has disrupted the traditional taxi industry.
Netflix
 Netflix is another example of how information systems can be used for competitive advantage. The company has disrupted the entertainment industry by using information systems to personalize their content recommendations and provide a seamless viewing experience across multiple devices.
Netflix is another example of how information systems can be used for competitive advantage. The company has disrupted the entertainment industry by using information systems to personalize their content recommendations and provide a seamless viewing experience across multiple devices.
One of the key ways that Netflix has used information systems for competitive advantage is through the use of data analytics. The company collects a vast amount of data on customer preferences, viewing behavior, and market trends, which they use to continually refine and improve their content offerings. For example, they use data analytics to monitor which shows are being watched, how long viewers are watching for, and which shows are being recommended to them. This has enabled them to tailor their content offerings to the preferences of their customers, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Another way that Netflix has used information systems for competitive advantage is through the use of technology. By providing a seamless viewing experience across multiple devices, Netflix has created a user-friendly and convenient platform that has made it easier for viewers to access their content. They also use technology such as predictive algorithms and advanced analytics to ensure that their content is engaging and relevant to their viewers.
Finally, Netflix has used information systems to optimize their supply chain, reducing costs and providing a competitive advantage in the market. By using real-time analytics, Netflix is able to track viewer behavior and optimize their content production and delivery processes, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
Netflix’s use of information systems has enabled them to create a platform that is personalized, user-friendly and efficient, providing a unique value proposition in the entertainment industry. By using data analytics and technology, they have been able to optimize their content offerings and improve the customer experience, providing a competitive advantage that has disrupted traditional television networks.
Zara
 Zara is a Spanish clothing and accessories retailer that is known for its fast fashion approach. The company is a part of the Inditex group and was founded in 1975. Zara has been able to gain a competitive advantage in its industry by using information systems strategically.
Zara is a Spanish clothing and accessories retailer that is known for its fast fashion approach. The company is a part of the Inditex group and was founded in 1975. Zara has been able to gain a competitive advantage in its industry by using information systems strategically.
Zara’s supply chain management strategy is the core of its business model. The company has been able to create a fast and responsive supply chain by using an innovative information system. The information system is used to track the inventory levels of each store in real time. This allows the company to quickly identify which products are selling and which products are not. The information system also helps the company to quickly respond to changes in customer demand.
One of the key advantages of the information system used by Zara is that it allows the company to get new products to market faster than its competitors. The company is able to design, manufacture, and deliver new products to stores within two weeks. This is a fraction of the time it takes for other retailers to get new products to market. The information system used by Zara allows the company to respond quickly to changes in customer preferences and to deliver products that meet those preferences.
Another advantage of Zara’s information system is that it allows the company to reduce waste and inventory costs. The company only produces products that it knows will sell. This allows the company to keep its inventory levels low, which reduces the amount of money tied up in inventory. The information system also allows the company to quickly identify products that are not selling and to make adjustments to its production and distribution strategies accordingly.
Zara’s use of information systems has helped the company to stay ahead of its competitors. The company’s fast and responsive supply chain has allowed it to create a unique value proposition for its customers. The company’s ability to get new products to market quickly and to respond quickly to changes in customer preferences has helped it to maintain its competitive advantage in the retail industry.
Tesla
 Tesla is a leading electric vehicle and energy company that was founded in 2003. The company has been able to gain a competitive advantage in its industry by using information systems strategically. Tesla’s innovative use of information systems has helped the company to create a unique value proposition for its customers and to stay ahead of its competitors.
Tesla is a leading electric vehicle and energy company that was founded in 2003. The company has been able to gain a competitive advantage in its industry by using information systems strategically. Tesla’s innovative use of information systems has helped the company to create a unique value proposition for its customers and to stay ahead of its competitors.
One of the key advantages of Tesla’s information systems is its use of data analytics. The company collects vast amounts of data from its vehicles and uses machine learning algorithms to analyze the data. This allows Tesla to identify patterns and insights that can help improve its vehicles and services. Tesla uses this information to continuously improve the performance and efficiency of its vehicles, which gives the company a competitive advantage in the electric vehicle industry.
Another advantage of Tesla’s information systems is its use of a centralized software platform. Tesla’s vehicles are connected to a centralized software platform that allows the company to remotely update and improve the features and performance of its vehicles. This means that Tesla’s vehicles are always up to date with the latest software improvements and enhancements, giving the company a competitive advantage in the constantly evolving electric vehicle market.
Tesla is also using information systems to create a unique customer experience. Tesla’s mobile app allows customers to remotely control and monitor their vehicles. This includes features such as remotely starting the vehicle, adjusting the temperature, and monitoring the vehicle’s location and charging status. This provides customers with an enhanced level of convenience and control over their vehicles, which helps to differentiate Tesla from its competitors.
Finally, Tesla is using information systems to create a sustainable energy ecosystem. Tesla’s energy products, such as solar panels and energy storage systems, are integrated with its electric vehicles and connected to a centralized software platform. This allows Tesla to optimize the use of renewable energy and reduce the reliance on fossil fuels. This sustainability-focused approach helps Tesla to create a unique value proposition for its customers and differentiate itself from its competitors.
In conclusion, Tesla’s strategic use of information systems has helped the company to gain a competitive advantage in the electric vehicle and energy industry. By leveraging data analytics, a centralized software platform, and a customer-centric approach, Tesla is able to continuously improve its products and services and create a unique value proposition for its customers.
Effects of Timing and Barriers to Entry on Competitive Advantage
Timing of Technology Adoption
The timing of technology adoption can have a significant impact on a company’s ability to gain a competitive advantage. Early adopters of new technologies often have a first-mover advantage, as they are able to establish themselves as leaders in the market and gain market share before competitors can catch up. However, there is also a risk involved in being an early adopter, as new technologies may not always be successful or may require significant investment in research and development.
 For example, Apple gained a competitive advantage with the introduction of the iPhone in 2007. By being an early mover in the smartphone market, Apple was able to establish itself as a leader in the industry and gain a significant market share before competitors like Samsung and Google could catch up. Additionally, Apple’s closed ecosystem, which included both hardware and software, provided a unique user experience that was difficult for competitors to replicate.
For example, Apple gained a competitive advantage with the introduction of the iPhone in 2007. By being an early mover in the smartphone market, Apple was able to establish itself as a leader in the industry and gain a significant market share before competitors like Samsung and Google could catch up. Additionally, Apple’s closed ecosystem, which included both hardware and software, provided a unique user experience that was difficult for competitors to replicate.
Being a first mover isn’t always a guarantee of competitive advantage. A counter example of a company who was a late entry but managed to gain competitive advantage is Netflix. Although Blockbuster was the dominant player in the video rental market, Netflix was able to disrupt the industry by introducing a new business model that offered online streaming of movies and TV shows. By focusing on customer experience and investing heavily in technology, Netflix was able to gain market share and establish itself as a leading provider of streaming services, ultimately leading to the downfall of Blockbuster. Despite being a late entry, Netflix was able to capitalize on the shift towards digital media and gain a sustainable competitive advantage through its innovative business model and use of technology.
Barriers to Entry
Another factor that can affect a company’s ability to gain a competitive advantage through technology is barriers to entry. Some technologies may require specialized knowledge or expertise, making it difficult for new entrants to compete with established players. Additionally, some technologies may require significant investments in infrastructure or equipment, making it difficult for small companies to compete with larger, more established players.
 One example of a company that gained a competitive advantage with barriers to entry is Tesla. Tesla’s electric vehicle technology required significant investments in research and development, as well as specialized expertise in battery technology and electric motor design. These barriers to entry made it difficult for new entrants to compete with Tesla, allowing the company to establish a dominant position in the electric vehicle market. Additionally, Tesla’s direct-to-consumer sales model and brand image as a luxury electric vehicle manufacturer further strengthened its competitive advantage.
One example of a company that gained a competitive advantage with barriers to entry is Tesla. Tesla’s electric vehicle technology required significant investments in research and development, as well as specialized expertise in battery technology and electric motor design. These barriers to entry made it difficult for new entrants to compete with Tesla, allowing the company to establish a dominant position in the electric vehicle market. Additionally, Tesla’s direct-to-consumer sales model and brand image as a luxury electric vehicle manufacturer further strengthened its competitive advantage.
Finally, a company’s ability to gain a sustainable competitive advantage through technology depends on its ability to continually innovate and adapt to new technologies. Technology is constantly evolving, and companies that fail to keep up with the latest trends and developments may find themselves at a disadvantage. To stay competitive, companies must invest in research and development, build partnerships with technology vendors, and stay abreast of emerging technologies in their industry.
One example of a company that has retained a competitive advantage through continual innovation is Google. Google’s success can be attributed to its constant innovation and development of new technologies and products, such as search engine algorithms, online advertising platforms, and cloud computing services. The company’s ability to stay ahead of competitors and meet the changing needs of its customers has allowed it to maintain its position as a leader in the tech industry. Additionally, Google’s emphasis on employee creativity and innovation, seen in its “20% time” policy, has fostered a culture of continual improvement and advancement.
IS Business Considerations
Organizations should consider the business implications of implementing an information system because it can provide a competitive advantage in the industry. The case studies of Zara and Tesla demonstrate how strategic use of information systems can lead to improved supply chain management, faster time to market, reduced waste and inventory costs, improved performance and efficiency, enhanced customer experience, and differentiation from competitors.
Implementing an information system requires significant investment, so it is crucial for organizations to evaluate the potential benefits and risks before making a decision. Organizations should also consider the impact on their business processes, organizational structure, and human resources, and ensure that they have the necessary resources, skills, and capabilities to effectively implement and manage the information system. Ultimately, the goal is to leverage the information system to achieve business objectives, meet customer needs, and stay ahead of the competition.
Summary
In today’s fast-paced business environment, companies are constantly looking for ways to gain competitive advantage. Using information systems (IS) can be an efficient way to achieve this goal. IS can provide businesses with a range of benefits, such as improved efficiency, better decision-making and enhanced customer service. However, to realize these benefits, companies must carefully consider a range of business considerations.
One of the most important considerations is the strategic alignment between IS and business objectives. A clear understanding of business objectives and how technology can support them is crucial. Implementing IS can be expensive, and businesses must evaluate how the technology will generate revenue and reduce costs. Companies should weigh the costs of implementation, maintenance, and upgrades against the expected return on investment. The implementation of IS must be cost-effective, and companies must ensure that the investment in the technology aligns with the budget and financial objectives. The implementation of IS must be driven by business needs and not the other way around. A lack of alignment between business objectives and IS can lead to inefficient processes, wasted resources, and lost opportunities.
Discussion Questions:
- How can companies ensure that there is strategic alignment between business objectives and IS?
- How can the use of IS improve customer service and enhance the customer experience?
- What are the potential risks and challenges associated with the use of IS for competitive advantage?
- How can businesses ensure that their IS is flexible enough to accommodate future technological changes and advancements?
- What are some effective ways to train employees on the use of IS?
- How can companies prioritize the protection of data and confidential information in the use of IS?
- What are the most important factors that companies should consider when selecting appropriate technology?
- How can businesses evaluate the cost-effectiveness of implementing IS?
- What are the most important policies and procedures that should be established for the use of IS?
- How can the effective governance and management of IS contribute to competitive advantage?

