Learning Objectives
Describe the similarities and differences among eight general types of nonverbal communication.
Now that we have discussed the general principles that apply to nonverbal communication let’s examine eight types of nonverbal communication to further understand this challenging aspect of communication:
- Space
- Time
- Physical characteristics
- Body movements
- Touch
- Paralanguage
- Artifacts
- Environment
Space
When we discuss space in a nonverbal context, we mean the space between objects and people. Space is often associated with social rank and is an important part of business communication. Who gets the corner office? Why is the head of the table important, and who gets to sit there?
People from diverse cultures may have different normative space expectations. If you are from a large urban area, having people stand close to you may be normal. If you are from a rural area or a culture where people expect more space, someone may be standing “too close” for comfort and not know it.
Edward T. Hall, serving in the European and South Pacific Regions in the Corps of Engineers during World War II, traveled around the globe. As he moved from one place to another, he noticed that people in different countries kept different distances from each other. In France, they stood closer to each other than they did in England. Hall wondered why that was and began to study what he called proxemics, or the study of the human use of space and distance in communication (Hall, E. T., 1963).
In The Hidden Dimension, Hall indicated two main aspects of space: territory and personal space. He drew on anthropology to address the concepts of dominance and submission and noted that the more powerful person often claims more space. Space plays an important role in modern society, from who gets the corner office to how we negotiate space between vehicles. Road rage is increasingly common where overcrowding occurs, and as more vehicles occupy the same roads, tensions over space are predictable.
Territory is related to control. To establish control over your room, maybe you painted it your favorite color or put up posters that represent your interests or things you consider unique about yourself. Families or households often mark their space by putting up fences or walls around their houses. This sense of a right to control your space is implicit in territory. Territory means the space you claim as your own, are responsible for or are willing to defend.
The second aspect Hall highlights is personal space, or the “bubble” of space surrounding each individual. As you walk down a flight of stairs, which side do you choose? We may choose the right side because we’ve learned that is what is expected, and people coming up the same stair choose their right. The right choice ensures that personal space is not compromised. But what happens when someone comes up the wrong side? They violate the understood rules of movement and often correct themselves. But what happens if they don’t change lanes as people move up and down the stairs? They may get dirty looks or even get bumped as people in the crowd handle the invasion of “their” space. There are no lane markers, and bubbles of space around each person move with them, allowing for the possibility of collision.
We recognize the basic need for personal space, but the normative expectations for space vary greatly by culture. You may perceive that in your home, people sleep one to each bed, but in many cultures, people sleep two or more to a bed, which is considered normal. If you were to share that bed, you might feel uncomfortable, while someone raised with group sleeping norms might feel uncomfortable sleeping alone. From where you stand in an aerobics class in relation to others to where you place your book bag in class, your personal expectations of space are often at variance with others.
As the context of a staircase has norms for nonverbal behavior, so does the public speaking context. In North America, eye contact with the audience is expected. Big movements and gestures are not generally expected and can be distracting. The speaker occupies a space on the “stage,” even if it’s in front of the class. When you occupy that space, the audience will expect to behave in certain ways. If you talk to the screen behind you while displaying a PowerPoint presentation, the audience may perceive that you are not paying attention to them. Speakers are expected to pay attention to and interact with the audience, even if the feedback is primarily nonverbal. Your movements should coordinate with your speech’s tone, rhythm, and content. Pacing back and forth, keeping your hands in your pockets, or crossing your arms may communicate nervousness, or even defensiveness, and detract from your speech.
Time
Do you know what time it is? How aware you are of time varies by culture and normative expectations of adherence (or ignorance) of time. Some people and the communities and cultures they represent are very time-oriented. The Euro Railways trains in Germany are famous for departing and arriving according to the schedule. In contrast, if you take the train in Argentina, you’ll find that the schedule is more of an approximation of when the train will leave or arrive.
“Time is money” is a common saying across many cultures, revealing the high value of time. In social contexts, it often reveals social status and power. Who are you willing to wait for? A doctor for an office visit when you are sick? A potential employer for a job interview? Your significant other or children? Sometimes, we get impatient, underscoring our value for time.
When you give a presentation, does your audience have to wait for you? Time is a relevant factor in the communication process in your speech. The best way to show your audience respect is to honor the time expectation associated with your speech. Always try to stop speaking before the audience stops listening; if the audience perceives that you have “gone over time,” they will be less willing to listen. This, in turn, will have a negative impact on your ability to communicate your message.
Suppose you are presenting a speech that has three main points. Your audience expects you to regulate the time and attention to each point, but if you spend all your time on the first two points and rush through the third, your speech won’t be balanced and will lose rhythm. The speaker occupies a position of some power, but the audience gives them that position. You will move through your points more effectively by displaying respect and maintaining balance.
Chronemics is the study of how we refer to and perceive time. Tom Bruneau at Radford University has spent a lifetime investigating how time interacts with communication and culture (Bruneau, T., 1974; Bruneau, T., 1990; Bruneau, T., and Ishii S., 1988). He notes that time is often considered the equivalent of money across Western society. The value of speed is highly prized in some societies (Schwartz, T., 1989). In others, there is a great respect for slowing down and taking a long-term view of time.
When you order a meal at a fast food restaurant, what are your expectations for how long you will have to wait? When you order a pizza online for delivery, when do you expect it to arrive? If you order cable service for your home, when do you expect it to be delivered? In the first case, you might measure the delivery of a hamburger in a matter of seconds or minutes and perhaps thirty minutes for pizza delivery, but you may measure the time from your order to working cable in days or even weeks. You may even have to be at your home from 8 a.m. to noon, waiting for its installation. The expectations vary by context, and we often grow frustrated in a time-sensitive culture when the delivery does not match our expectations.
In the same way, how long should it take to respond to a customer’s request for assistance or information? How long should they be on hold if they call on the phone? How soon should they expect a response to an e-mail? As a skilled business communicator, you will know to anticipate normative expectations and do your best to meet those expectations more quickly than anticipated. Your prompt reply or offer of help in response to a request, even if you cannot solve the issue on the spot, is often regarded positively, contributing to the formation of positive communication interactions.
Across cultures, the value of time may vary. Some Mexican American friends may invite you to a barbecue at 8 p.m., but when you arrive, you are the first guest because it is understood that the gathering actually doesn’t start until after 9 p.m. Similarly, in France, an 8 p.m. party invitation would be understood to indicate you should arrive around 8:30, but in Sweden, 8 p.m. means 8 p.m., and latecomers may not be welcome. Some Native Americans, particularly elders, speak in well-measured phrases and take long pauses between phrases. They do not hurry their speech or compete for their turn, knowing no one will interrupt them (McLean, S., 1998). Some Orthodox Jews observe religious days when they do not work, cook, drive, or use electricity. People around the world have different ways of expressing value for time.
Physical Characteristics
You didn’t choose your birth, your eye color, the natural color of your hair, or your height, but people spend millions every year trying to change their physical characteristics. You can get colored contacts, dye your hair, and buy shoes to raise your stature a couple of inches if you are shorter than you’d like to be. You won’t be able to change your birth, and no matter how much you stoop to appear shorter, you won’t change your height until time and age gradually make itself apparent. If you are tall, you might find the correct shoe size, pant length, or even the length of the mattress a challenge, but there are rewards. Have you ever heard that taller people get paid more (Burnham, T., and Phelan, J., 2000)? There is some truth to that idea. There is also some truth to the notion that people prefer symmetrical faces (where both sides are equal) over asymmetrical faces (with unequal sides, like a crooked nose or having one eye or ear slightly higher than the other) (Burnham, T., and Phelan, J., 2000).
We often judge a person’s personality or behavior based on physical characteristics, and researchers quickly note that those judgments are often inaccurate (Wells, W., and Siegel, B., 1961; Cash, T., and Kilcullen, R., 1985). Being comfortable with yourself is an important part of your presentation, regardless of your eye or hair color or even how tall you are. Act naturally and consider aspects of your presentation you can control to maximize a positive image for the audience.
Body Movements
The study of body movements, called kinesics, is key to understanding nonverbal communication. Since your actions will significantly contribute to the effectiveness of your business interactions, let’s examine four distinct ways body movements complement, repeat, regulate, or replace your verbal messages.
Body movements can complement the verbal message by reinforcing the main idea. For example, you may give a customer an orientation presentation about a software program. As you say, “Click on this tab,” you may also initiate that action. Your verbal and nonverbal messages reinforce each other. You can also reinforce the message by repeating it. If you first say, “Click on the tab,” and then motion with your hand to the right, indicating that the customer should move the cursor arrow with the mouse to the tab, your repetition can help the listener understand the message.
In addition to repeating your message, body movements can also regulate conversations. Nodding your head to indicate that you are listening may encourage the customer to continue asking questions. Holding your hand up and palm out may signal them to stop and provide a pause where you can start to answer.
Body movements also substitute or replace verbal messages. Ekman and Friesen found that facial features communicate to others our feelings, but our body movements often reveal how intensely we experience those feelings (Ekman, P., and Friesen, W., 1967). For example, if the customer makes a face of frustration while trying to use the software program, they may need assistance. If they push away from the computer and separate themselves physically from interacting with it, they may be extremely frustrated. Learning to gauge feelings and their intensity as expressed by customers takes time and patience, and your attention to them will improve your ability to facilitate positive interactions.
Touch
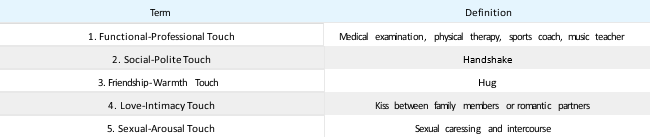
Touch in communication interactions is called haptics. In Table 11.2.1, William Seiler and Melissa Beall identify five distinct types of touch, from impersonal to intimate.
Before giving your presentation, you may interact with people by shaking hands and having casual conversations. This interaction can help establish trust before you take the stage. While speaking in public, we do not often touch people in the audience, but we do interact with visual aids, our note cards, and other objects. How we handle them can communicate our comfort level. It’s always a good idea to practice using the technology, visual aids, or note cards you will use in a speech during a practice session. Using the technology correctly by clicking the right mouse button or pressing the switch on the overhead projector can contribute to your credibility.
Paralanguage
Paralanguage is the exception to the definition of nonverbal communication. You may recall that we defined nonverbal communication as not involving words, but paralanguage exists when we speak and use words. Paralanguage involves verbal and nonverbal aspects of speech that influence meaning, including tone, intensity, pausing, and even silence.
Perhaps you’ve also heard of a pregnant pause, a silence between verbal messages that is full of meaning. The meaning itself may be hard to understand or decipher, but it is there nonetheless. For example, your coworker Jan comes back from a sales meeting speechless and with a ghost-white complexion. You may ask if the meeting went all right. “Well, ahh…” may be the only response you get. The pause speaks volumes. Something happened, though you may not know what. It could be personal if Jan’s report was not well received, or it could be more systemic, like the news that sales figures are off by 40 percent and pink slips may not be far behind.
Silence or vocal pauses can communicate hesitation, indicate the need to gather thought or serve as a sign of respect. Keith Basso quotes an anonymous source as stating, “It is not the case that a man who is silent says nothing” (Basso, K. A., 1970). Sometimes, we learn just as much, or even more, from what a person does not say as what they do say. In addition, both Basso and Susan Philips found that traditional speech among Native Americans places a special emphasis on silence (Philips, S., 1983).
Artifacts
Do you cover your tattoos when you are at work? Do you know someone who does? Or perhaps you know someone who has a tattoo and does not need to cover it up on their job? Expectations vary a great deal, but body art or tattoos are still controversial in the workplace. According to the San Diego Union-Tribune (Kinsman, M., 2001),
- 20 percent of workers indicated their body art had been held against them on the job.
- 42 percent of employers said the presence of visible body art lowered their opinion of workers.
- 44 percent of managers surveyed have body art.
- 52 percent of workers surveyed have body art.
- 67 percent of workers with body art or piercings cover or remove them during work hours.
In your line of work, a tattoo might be an important visual aid or detract from your effectiveness as a business communicator. Body piercings may express individuality, but you need to consider how employers and customers will interpret them.
Artifacts are forms of decorative ornamentation that are chosen to represent self-concept. They can include rings and tattoos but may also include brand names and logos. From clothes to cars, watches, briefcases, purses, and even eyeglasses, what we choose to surround ourselves with communicates something about our sense of self. They may project gender, role or position, class or status, personality, and group membership or affiliation. Paying attention to a customer’s artifacts can give you a sense of the self they want to communicate and may allow you to more accurately adapt your message to meet their needs.
Environment
Environment involves the physical and psychological aspects of the communication context. More than the tables and chairs in an office, the environment is an important part of the dynamic communication process. The perception of one’s environment influences one’s reaction to it. For example, Google is famous for its work environment, with spaces created for physical activity and even in-house food service around the clock. The expense is no doubt considerable, but Google’s actions speak volumes. The results produced in the environment, designed to facilitate creativity, interaction, and collaboration, are worth the effort.
Key Takeaway
Nonverbal communication can be categorized into eight types: space, time, physical characteristics, body movements, touch, paralanguage, artifacts, and environment.
Exercises
Do a Google search on space and culture. Share your findings with your classmates.
Note where people sit on the first day of class and each class session thereafter. Do students return to the same seat? If they do not attend class, do the classmates leave their seats vacant? Compare your results.
What kind of value do you have for time, and what is truly important to you? Make a list of what you spend your time on and what you value most. Do the lists match? Are you spending time on what is truly important to you? Relationships take time, and if you want them to succeed in a personal or business context, you must prioritize them.
To what degree is time a relevant factor in communication in the information age? Give some examples. Discuss your ideas with a classmate.
How many people do you know who have chosen tattoos or piercings as a representation of self and a statement of individuality? Survey your friends and share your findings with your classmates.
Basso, K. A. (1970). To give up on words: Silence in western Apache culture. In D. Carbaugh (Ed.), Cultural communication and intercultural contact (pp. 301–318). Hillsdale, NJ: Laurence Erlbaum.
Bruneau, T., & Ishii, S. (1988). Communicative silence: East and west. World Communication, 17, 1–33.
Burnham, T., & Phelan, J. (2000). Mean genes: From sex to money to food: Taming our primal instincts. Cambridge, MA: Perseus.
Bruneau, T. (1974). Time and nonverbal communication. Journal of Poplular Culture, 8, 658–666.
Bruneau, T. (1990). Chronemics: The study of time in human interaction. In J. DeVito & M. Hecht (Eds.), The nonverbal reader (pp. 301–311). Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press.
Cash, T., & Kilcullen, R. (1985). The eye of the beholder: Susceptibility to sexism and beautyism in the evaluation of managerial applicants. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 15, 591–605.
Ekman, P., & Friesen, W. (1967). Head and body cures in the judgment of emotions: A reformulation. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 24, 711–724.
Hall, E. (1966). The hidden dimension. New York, NY: Doubleday.
Hall, E. T. (1963). Proxemics: The study of man’s spacial relations and boundaries. In Iago Galdston (Ed.), Man’s image in medicine and anthropology (pp. 422–445). New York, NY: International Universities Press.
Kinsman, M. (2001, August 20). Tattoos and nose rings. San Diego Union-Tribune, p. C1.
McLean, S. (1998). Turn-taking and the extended pause: A study of interpersonal communication styles across generations on the Warm Springs Indian reservation. In K. S. Sitaram & M. Prosser (Eds.), Civic discourse: Multiculturalsim, cultural diversity, and global communication (pp. 213–227). Stamford, CT: Ablex Publishing Company.
Philips, S. (1983). The invisible culture: Communication in the classroom and community on the Warm Springs Indian Reservation. Chicago, IL: Waveland Press.
Schwartz, T. (1989, January/February). Acceleration syndrome: Does everyone live in the fast lane? Utne Reader, 31, 36–43.
Seiler, W., & Beall, M. (2000). Communication: Making connections (4th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Wells, W., & Siegel, B. (1961). Stereotypes somatypes. Psychological Reports, 8, 77–78.
This page titled 11.2: Types of Nonverbal Communication is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Anonymous (LibreTexts Staff), from which source content was edited to the style and standards of the Pressbook platform licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License by Brandi Schur.

