9 Arts Engagement in Nursing: A Holistic Approach to Mental Health
Learning Objectives
- Explain the benefits of arts engagement for mental health across the socio-ecological model.
- Identify examples of art-based population health interventions and their impact on specific populations.
- Analyze the challenges and considerations of integrating arts into nursing practice.
- Apply principles of trauma-informed care and person-centered care when considering the use of art-based interventions.
Arts Engagement in Nursing: A Holistic Approach to Mental Health
Integrating arts-based activities into nursing education and practice offers a valuable tool to promote holistic patient care, specifically in addressing mental health needs. Several sources highlight the benefits of art engagement as a protective and rehabilitative behavior for mental health (Rodriguez et al., 2024). Arts-based interventions can positively impact mental health across various socio-ecological levels.
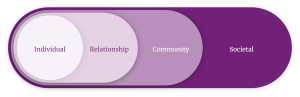
Figure 9-1 Socio-Ecological Model
Note: Centers for Disease Control (2024). Violence Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/violence-prevention/about/index.html#print
Individual Level: Engaging in arts, such as music and dance, positively impacts stress reduction, mood regulation, and self-esteem (Rodriguez et al., 2024). These activities offer avenues for emotional expression and coping mechanisms, crucial for individuals experiencing mental distress (Milason et al., 2024; Raimie et al., 2024).
Interpersonal Level: Arts-based activities can facilitate communication and connection, reducing loneliness and promoting social support (Milason et al., 2024; Raimie et al., 2024). This approach is particularly relevant in mental health care, where therapeutic relationships are essential (Milason et al., 2024).
Community Level: Arts engagement can empower communities, promote health literacy, and foster social cohesion9. This approach can address mental health stigma and promote a sense of belonging among individuals with shared experiences (Rodriguez et al., 2024).
Policy Level: Policies supporting arts engagement, like social prescribing, can bridge the gap between clinical and community resources, particularly for marginalized communities10. Social prescribing connects individuals to non-clinical services, including arts participation, to address social determinants of health (Rodriguez et al., 2024).
Cultural Level: Recognizing cultural ecologies within communities highlights the need for culturally responsive art-based initiatives (Rodriguez et al., 2024). This approach ensures that interventions are tailored to the specific needs and values of diverse populations (Rodriguez et al., 2024).
Examples of Art-Based Population Health Interventions
Project: Music Heals Us: This program provides interactive music programming and performances to marginalized communities, including disabled, elderly, homeless, and incarcerated populations. (Rodriguez et al., 2024). This initiative demonstrates arts engagement at the community level, enhancing health literacy and community empowerment (Rodriguez et al., 2024).
CultureRx: This social prescribing pilot program in Massachusetts connects healthcare providers with cultural organizations to offer free arts and culture experiences to patients (Rodriguez et al., 2024). CultureRx emphasizes the role of policy in promoting equitable access to arts-based resources, ultimately improving health outcomes (Rodriguez et al., 2024).
Integrating Arts into Nursing Education
Nursing education needs to embrace innovative pedagogical approaches to equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge to address the growing mental health crisis. One study explored the use of an immersive, trauma-informed, art-based VR environment to teach mental health nursing students about trauma (Milason et al., 2024). The study found that combining art, technology, and lived experiences facilitated authentic learning and deeper reflection among students (Milason et al., 2024).
Furthermore, integrating practical experiences with arts-based activities is essential. One university offered a creative health placement where nursing students engaged in art practices and facilitated creative health cafes for the public (Ridgway et al., 2024). This placement challenged students’ perceptions of nursing and highlighted the value of creative health in promoting person-centered care (Ridgway et al., 2024).
Challenges and Considerations
- Underutilization of Arts in Mental Health Nursing: Despite the acknowledged benefits, art-based interventions remain underutilized in mental health nursing practice (Milason et al., 2024). This underutilization could be attributed to a lack of awareness, training, resources, and time constraints (Milason et al., 2024).
- Safety Concerns: Employing art-based interventions in secure mental health settings requires careful consideration of safety protocols to mitigate potential risks associated with art materials (Milason et al., 2024).
- Individual Preferences: While art engagement can be beneficial, it is crucial to recognize individual preferences and choices, as arts may not be a universal solution for everyone (Milason et al., 2024).
Conclusion
Arts engagement is a powerful tool that can contribute significantly to a holistic approach to mental health care. Integrating arts into nursing education and practice can empower nurses to address the multifaceted needs of individuals experiencing mental distress, promoting well-being and recovery across various social-ecological levels. Future research should explore the long-term impacts of art-based interventions on both patients and nursing professionals and develop standardized guidelines for implementing these approaches within healthcare settings.
Reflection Journal Questions:
Reflecting on your own personal experiences, how might incorporating creative activities into nursing practice enhance person-centered care and improve mental health outcomes for diverse populations?
- Consider specific examples of how you might integrate these activities into various healthcare settings and the potential challenges and benefits you anticipate.
How can nurses leverage their understanding of population mental health to promote a more equitable and holistic approach to healthcare that addresses the social determinants of health?
- Consider the role of nurses in connecting patients with community resources and advocating for policies that support social prescribing initiatives.
Glossary
- Art-Based Interventions: The use of creative arts activities, such as music, dance, visual arts, and creative writing, to promote mental and emotional well-being.
- Social Prescribing: A practice where healthcare providers connect patients with non-clinical services, including arts engagement and community resources, to address social determinants of health.
- Creative Health: The use of arts and creative practices to improve health and well-being, encompassing a wide range of activities, including arts on prescription and community-based art programs.
- Trauma-Informed Care: An approach that recognizes the widespread impact of trauma and emphasizes physical, psychological, and emotional safety for individuals who have experienced trauma.
- Holistic Care: An approach to healthcare that addresses the physical, emotional, social, and spiritual needs of the individual.
- Person-Centered Care: An approach to care that focuses on the individual’s needs, preferences, and values, empowering them to actively participate in their care.
- Mental Health Inequities: Disparities in the prevalence, access to care, and quality of mental health services experienced by different populations, often rooted in social determinants of health and systemic barriers.
NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1
A nurse is caring for a patient experiencing anxiety and depression. Which of the following art-based interventions would be most appropriate for the nurse to suggest?
a) Attending a support group focused on medication management
b) Participating in a guided meditation session
c) Engaging in a painting class at a local community center
d) Reading a self-help book on cognitive behavioral therapy
Question 2
A nursing student is learning about social prescribing. Which of the following is an example of a service that could be offered through social prescribing?
a) Referral to a specialist for a medical diagnosis
b) Prescription for an antidepressant medication
c) Enrollment in a community gardening program
d) Admission to an inpatient psychiatric facility
Question 3
A nurse is developing a trauma-informed care plan for a patient with a history of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Which of the following principles should guide the nurse’s approach?
a) Focusing primarily on symptom management through medication
b) Avoiding discussions about past traumatic experiences
c) Prioritizing the patient’s sense of safety and control
d) Emphasizing the importance of confronting traumatic memories
Question 4
A group of nursing students is discussing the benefits of creative health placements. Which of the following statements demonstrates an understanding of the value of these placements?
a) “Creative health placements are primarily focused on teaching students about art therapy techniques.”
b) “Creative health placements can help students develop a deeper understanding of person-centered care.”
c) “Creative health placements are designed to replace traditional clinical placements in acute care settings.”
d) “Creative health placements are only beneficial for students interested in pursuing careers in mental health nursing.”
Question 5
A nurse is advocating for the integration of arts into mental health care policies. Which of the following statements accurately reflects the rationale for this advocacy?
a) “Arts engagement can replace the need for traditional mental health treatments, such as medication and therapy.”
b) “Arts engagement is only effective for individuals with a strong background in the arts.”
c) “Arts engagement can promote mental well-being, reduce stigma, and enhance community resilience.”
d) “Arts engagement should be limited to hospital settings to ensure patient safety.”
Question 6
A nurse is working with a community organization to develop a culturally responsive art-based program for a diverse population. Which of the following considerations should be prioritized?
a) Designing a program based on the nurse’s personal artistic preferences
b) Selecting art materials that are readily available and inexpensive
c) Ensuring that the program reflects the cultural values and beliefs of the community
d) Implementing a standardized art curriculum used in other community settings
References:
Milasan, L. H., Farr, A., Turnbull, I., & Scott-Purdy, D. (2024). Behind the creative canvas: An innovative trauma-informed art-based educational approach using an immersive learning pedagogy. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing, 33, 431–441. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/inm.13250
Raja Raimie, R.E., Sabran, M.K., & Azraai, N.Z. (2024). Media Art in Healthcare Environments: Enhancing Student’s Well-being and Mental Health. International Journal of Art and Design. doi:10.24191/ijad.v8i1.1391
Ridgway, V., Henshaw, R., Davies, C., Faulkner, G., Marsh, V., & Stonley, L. (2024). Creative health: challenging student nurses to learn from the arts. Nursing Times [Online], 120(4). https://www.nursingtimes.net/education-and-training/creative-health-challenging-student-nurses-to-learn-from-the-arts-11-03-2024/
Rodriguez, A. K., Akram, S., Colverson, A. J., Hack, G., Golden, T. L., & Sonke, J. (2024). Arts Engagement as a Health Behavior: An Opportunity to Address Mental Health Inequities. Community health equity research & policy, 44(3), 315–322. https://doi.org/10.1177/2752535X231175072

